Insect Bite Scar Treatment Guide
Select the characteristics of your insect bite scar to get personalized treatment recommendations:
Flat Scar
No raised texture, may have slight discoloration
Raised Scar
Bump above skin level, may be red or pink
Dark Spot
Darker than surrounding skin, flat
Painful Bump
Thick, hard, and painful scar tissue
Treatment Options Overview
| Treatment | Best For | Effectiveness | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| At-Home Care | General maintenance | 3/5 | $10-$50 |
| Prescription Creams | Inflammation control | 4/5 | $20-$100 |
| Laser Therapy | Pigment and texture issues | 5/5 | $400-$1500/session |
| Cryotherapy | Thick scars | 3/5 | $150-$500 |
When an insect bite or sting leaves a mark that won’t fade, it can feel frustrating and even embarrassing. The good news is that most bite‑related scars respond well to a mix of simple at‑home steps and, if needed, professional care. Below you’ll find a step‑by‑step guide that covers prevention, everyday remedies, over‑the‑counter options, and when to seek a dermatologist.
Understanding What Happens After a Bite
After an insect pierces the skin, the body launches an immune response that often leaves a small wound. As the wound heals, fibroblasts produce scar tissue a dense bundle of collagen fibers that replaces normal skin after injury. If the bite was especially inflamed or you scratched it, the scar can become raised (hypertrophic) or darker (hyperpigmented). Knowing the type of scar you’re dealing with helps you pick the right treatment.
First‑Aid Tips to Minimize Scarring
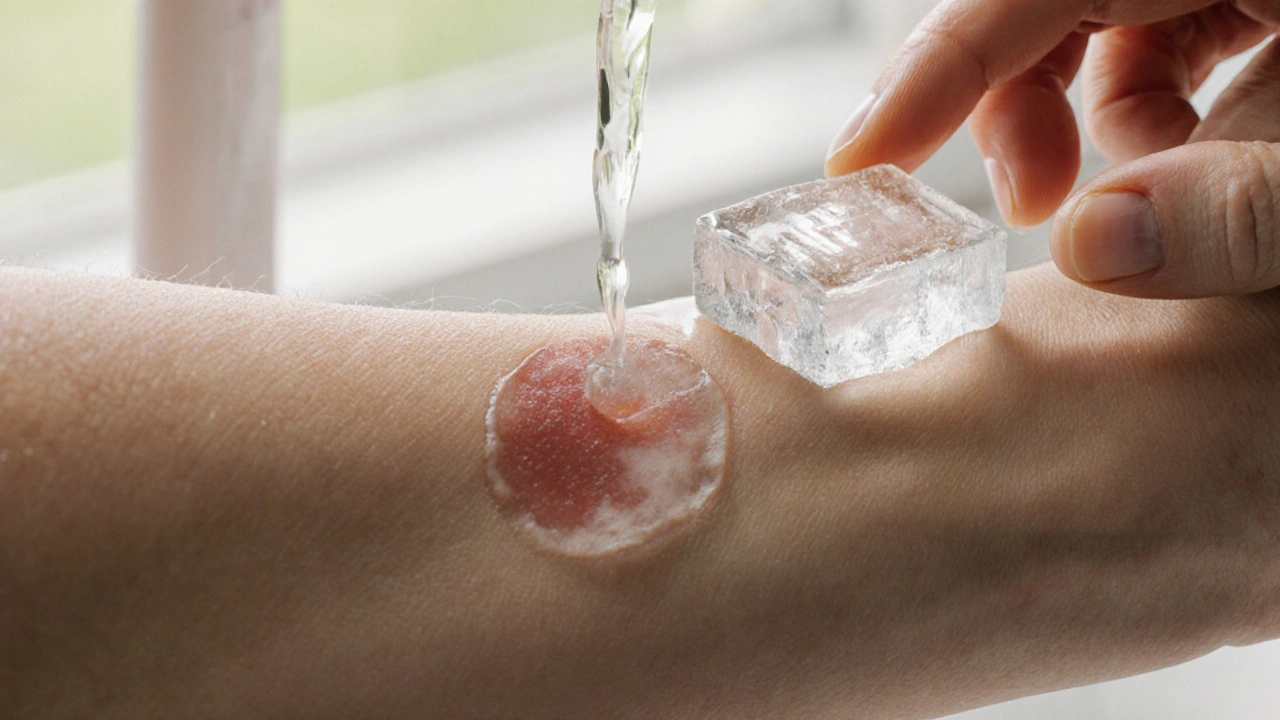
- Clean quickly: Wash the area with mild soap and water within minutes to reduce infection risk.
- Cold compress: Apply an ice pack for 10‑15 minutes to limit swelling and lessen the inflammatory cascade.
- Avoid scratching: Scratching re‑opens the wound and increases collagen deposition.
- Keep it moisturized: A thin layer of aloe vera gel a natural soothing agent that promotes cell turnover and reduces inflammation helps the skin regenerate more evenly.
These steps buy you time; the real work begins once the bite has crusted over and the skin starts to remodel (usually 3‑7 days after the bite).
At‑Home Remedies That Actually Work
Many over‑the‑counter ingredients have been studied for their scar‑softening properties. Below are the most evidence‑backed options and how to use them.
- Silicone gel sheets: Apply a silicone gel sheet a medical‑grade silicone polymer that creates a moist environment and flattens raised scars for 12‑14 hours daily. Clinical trials show a 30‑50% reduction in scar height after 8‑12 weeks.
- Vitamin C serum: Use a 10‑15% L‑ascorbic acid serum twice a day. Vitamin C interferes with melanin production, lightening hyperpigmented spots, and boosts collagen alignment.
- Honey: Apply raw Manuka honey as a thin mask for 20 minutes, then rinse. Its antibacterial properties keep the wound clean while its sugars support tissue remodeling.
- Exfoliating acids: A gentle 5% glycolic acid toner two to three times weekly removes dead skin cells, encouraging newer, smoother skin to surface.
Stick to a routine for at least 6weeks before judging effectiveness-scar remodeling is a slow process.
When to Reach for Pharmacy‑Grade Products
If home care isn’t enough, step up to these stronger options. All are safe for most skin types but read the label for contraindications (e.g., if you have eczema).
- Corticosteroid cream: A mild prescription‑strength 0.5% hydrocortisone can reduce inflammation in hypertrophic scars. Use under a dermatologist’s guidance for no longer than 2 weeks at a time.
- Onion extract gel (e.g., Mederma®): Contains allicin, which may soften scar tissue. Apply thinly twice daily for 12 weeks.
- Hydroquinone 2%: For stubborn dark spots, hydroquinone inhibits melanin synthesis. Limit use to 4‑6 months to avoid ochronosis.
Professional Treatments: What a dermatologist a medical specialist trained in skin health and cosmetic procedures can offer
When scars are thick, painful, or resistant to topical care, a dermatologist can provide targeted procedures. Below is a quick comparison of the most common options.
| Type | Effectiveness (1‑5) | Cost (AUD) | Typical Use | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone gel sheet | 4 | 30‑70 (per sheet) | Flat, raised scars | Non‑invasive, easy home use | Needs daily dedication |
| Laser therapy | 5 | 400‑1500 (per session) | Red or pigmented scars | Quick results, can improve texture | Multiple sessions, possible redness |
| Cryotherapy | 3 | 150‑500 | Thick hypertrophic scars | Reduces volume quickly | May cause temporary skin discoloration |
| Dermabrasion | 4 | 600‑1200 | Surface irregularities | Long‑lasting smoothing | Recovery time, risk of infection |
Laser therapy, especially fractional CO₂ or pulsed‑dye lasers, is often the go‑to for pigmented or raised scar tissue because it breaks down excess collagen while stimulating healthy skin growth. Cryotherapy works like a mini‑freeze: a probe delivers liquid nitrogen to the scar, causing the tissue to shrink. Dermabrasion mechanically sands the scar surface, paving the way for new epidermal cells.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Situation
Think of scar care as a decision tree. Start with the scar’s appearance, then match it to a treatment tier:
- Flat, faint discoloration: Vitamin C serum + sunscreen.
- Raised or textured scar: Silicone gel sheet, consider laser if stubborn.
- Thick, painful bump: Corticosteroid cream short‑term, followed by cryotherapy or dermabrasion.
Don’t forget sun protection. UV rays can darken scar pigmentation up to 2‑3 times faster. A broad‑spectrum SPF30+ sunscreen applied each morning is a must.

Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Skipping the waiting period: Many people expect instant results. Give each treatment at least 6‑8 weeks to show effect.
- Over‑scrubbing: Aggressive exfoliation can damage new skin and trigger more collagen buildup.
- Mixing too many actives: Using retinoids with potent acids can cause irritation, slowing healing.
- Neglecting allergies: Test a small patch of any new product for 24hours before full application.
By staying consistent and patient, you’ll see the scar fade more quickly and with less risk of lasting marks.
Quick Checklist for Scar‑Free Skin After an Insect Bite
- Clean the bite within minutes.
- Apply a cold compress for 10‑15 minutes.
- Use aloe vera or honey as a soothing base.
- Start silicone gel sheets once the wound closes.
- Follow with Vitamin C serum morning and night.
- Protect with SPF30+ daily.
- Schedule a dermatologist visit if scar is raised, painful, or doesn’t improve after 3 months.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use natural oils like coconut or olive oil on a bite scar?
Light oils can keep the skin moisturised but they don’t actively remodel scar tissue. If you enjoy the feel, apply a thin layer after your silicone sheet or Vitamin C serum, but don’t rely on them as the primary scar‑treatment.
How long does it usually take for a bite scar to fade?
Most mild scars soften noticeably within 8‑12 weeks when you follow a consistent regimen. Deeper or hypertrophic scars can need 6‑12 months, especially if professional procedures are involved.
Is it safe to use over‑the‑counter steroid creams for a week?
Short‑term (under 2 weeks) use of a low‑strength hydrocortisone cream is generally safe for reducing inflammation. Higher‑potency steroids should only be applied under medical supervision.
Will laser therapy remove the scar completely?
Laser treatment dramatically improves texture and color, but most scars won’t disappear entirely. The goal is to make the scar blend with surrounding skin.
Can sun exposure make a bite scar worse?
Yes. UV rays trigger melanin production, deepening hyperpigmentation. Applying sunscreen daily helps keep the scar’s color from darkening.

Matt Quirie
October 10, 2025 AT 21:17First‑aid measures are essential, therefore, cleanse the bite promptly, apply a cold compress for ten to fifteen minutes, and avoid any scratching; these steps limit inflammation, reduce collagen overproduction, and set the foundation for optimal scar remodeling.
Pat Davis
October 15, 2025 AT 19:41Across various regions, the same principles apply: immediate hygiene, cold therapy, and diligent moisturisation with aloe vera or honey establish a barrier against infection and support the skin’s natural healing cascade, ultimately minimizing long‑term discoloration.
Mary Wrobel
October 20, 2025 AT 18:05Hey folks, think of your scar as a canvas-start with a splash of Vitamin C serum in the morning, a dab of soothing aloe at night, and protect the whole masterpiece with SPF 30; over weeks you’ll watch the pigment fade like watercolor under the sun.
Lauren Ulm
October 25, 2025 AT 16:29🔍 Some suggest that the "big pharma" narrative hides the truth: the real power lies in the body’s own electromagnetic field, which can be tuned with daily sunlight exposure 🕶️; align your circadian rhythm and the scar’s pigmentation may realign itself.
Michael Mendelson
October 30, 2025 AT 13:53One must recognise that the lay‑person’s approach is woefully inadequate; only a regimen anchored in clinically validated silicone sheets-applied with disciplined regularity-can truly elevate one's dermal aesthetic beyond the pedestrian.
Just Sarah
November 4, 2025 AT 12:17Considering the multifaceted nature of scar healing, could one not inquire whether a combined protocol of topical corticosteroids, followed by a structured laser schedule, might expedite collagen remodeling, thereby achieving superior outcomes?
Anthony Cannon
November 9, 2025 AT 10:41Silicone sheets are effective.
Kristie Barnes
November 14, 2025 AT 09:05Honestly, I’ve tried the sheets and they’re pretty low‑key easy-just slap ’em on after you’re done with your night cream and let them do their thing while you chill.
Zen Avendaño
November 19, 2025 AT 07:29From a collaborative standpoint, pairing gentle exfoliation with consistent sunscreen creates a synergy that encourages even pigment distribution without irritating the sensitive tissue.
Michelle Guatato
November 24, 2025 AT 05:53Let’s not ignore the hidden agenda: the push for expensive laser sessions is a diversion orchestrated by elite clinics to keep us dependent on their proprietary tech while natural immunomodulation remains under‑utilised.
Gabrielle Vézina
November 29, 2025 AT 04:17While many declare these remedies flawless, one must question the absolute certainty of such claims; perhaps the truth dwells in the nuanced interplay of skin biology and societal expectations.
carl wadsworth
December 4, 2025 AT 02:41In the spirit of harmony, I suggest a balanced routine: start with a silicone gel sheet, supplement with Vitamin C serum, and, if budget permits, consider a single laser session under professional supervision.
Neeraj Agarwal
December 9, 2025 AT 01:05Precision matters: apply hydroquinone for four weeks, monitor skin response, and refrain from over‑use, as excessive application may lead to ochronosis.
Rose K. Young
December 13, 2025 AT 23:29Honestly, most of these tips are just hype; if you’re not seeing results after a month, stop wasting time and consult a professional-no point in dragging on a scar forever.
Christy Pogue
December 18, 2025 AT 21:53Yay! Keep that positivity flowing-every day you stick to your routine, you’re one step closer to smoother skin, and remember, confidence shines brighter than any scar ever could!
Helena Pearson
December 23, 2025 AT 20:17When we contemplate the ephemerality of a bite scar, we are invited to examine the very nature of impermanence, a theme that recurs throughout the tapestry of human experience.
Each tiny lesion, once a reminder of vulnerability, can become a canvas upon which we project our aspirations for renewal.
By employing a disciplined regimen-silicone sheets for structural support, Vitamin C for chromatic balance, and diligent photoprotection-we engage in a ritual of self‑care that transcends mere dermatology.
The act of applying moisturizer is, in essence, an affirmation of agency, a declaration that we are not passive recipients of fate.
Scientific literature underscores that consistent use of silicone for eight to twelve weeks yields a measurable flattening of hypertrophic tissue, reinforcing the principle that patience is a potent therapeutic agent.
Simultaneously, the antioxidant capacity of ascorbic acid mitigates melanin synthesis, gently coaxing hyperpigmentation toward a more harmonious hue.
Yet, technology beckons with lasers that reshape collagen architecture, offering a glimpse into the future where scar reduction becomes a precise, controlled process.
Nonetheless, we must temper enthusiasm with caution, recognizing that each intervention carries its own risk profile and may not be universally appropriate.
From a philosophical perspective, the scar serves as a narrative fragment, a reminder that healing is iterative, not instantaneous.
Incorporating sun protection-SPF 30 or higher-into our daily ritual guards against the re‑darkening of pigment, reflecting the broader truth that vigilance guards against regression in all aspects of life.
Moreover, the communal sharing of experiences on platforms such as this cultivates a collective wisdom, fostering a supportive ecosystem for those navigating the post‑bite journey.
When we recount personal successes, we empower others to persist, illustrating the ripple effect of individual commitment.
Thus, the convergence of evidence‑based practice, mindfulness, and communal solidarity forms a robust framework for scar amelioration.
Embrace each step, honor the process, and remember that even the faintest mark can, over time, become a testament to resilience 😊.